
Periprosthetic joint infection calprotectin loosening metallosis wear disease.Ĭopyright © 2023, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. If PJI is unlikely, the calprotectin LFT can be applied as a further exclusion tool as the negative predictive value remains relatively high. The diagnostic accuracy of synovial calprotectin is impaired if moderate to severe signs of implant loosening are present. No correlation between the extent of osteolysis and false classification by means of the calprotectin assay was observed.

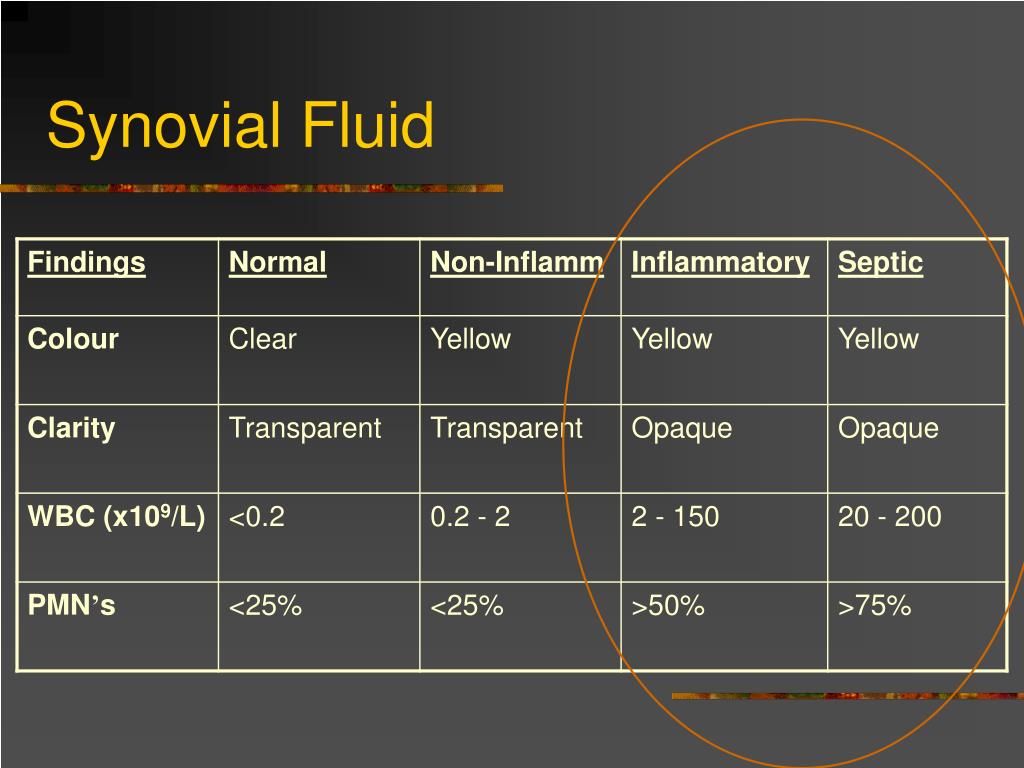
The calprotectin assay resulted in nine false positive and four false negative cases. The calprotectin assay yielded a sensitivity of 0.60, a specificity of 0.61, a positive predictive value of 0.40, and a negative predictive value of 0.78. Ten patients were classified as confirmed infections according to the EBJIS definition (7 THA and 5 TKA). Statistic quality criteria were calculated and compared using a binary classification test. Synovial white blood cell count (WBC), percentage of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMC), serum C-reactive protein (CRP) and synovial calprotectin using a lateral-flow-assay were tested against the European Bone and Joint Infection Society (EBJIS) definition for PJI. The extent of osteolysis was classified according to Engh et al., Paprosky et al., and the modern Knee Society Radiographic Evaluation and Scoring System. Thirty-three patients were included in this prospective study between February of 2019 and November of 2021. The purpose of this study was to evaluate calprotectin for the diagnosis of PJI in cases that preoperatively demonstrate moderate to severe periprosthetic osteolysis or implant migration as signs for implant loosening in THA and TKA. Concerns have already been raised in cases with metallosis and severe periprosthetic osteolysis because wear-induced inflammation may yield false positive results. However, its diagnostic utility has not been evaluated explicitly in cases with marked loosening or migration of the implant. Removing some of the fluid decreases pressure in the joint and improves joint movement.Synovial calprotectin has been demonstrated as a promising biomarker for periprosthetic joint infections (PJI) in painful total hip (THA) and knee arthroplasties (TKA). Yellow/clear synovial uids are typical in nonin-ammatory effusions, whereas yellow/cloudy uids usually involve an inammatory processes. Other appearances may indicate various disease states.
Joint aspiration is diagnostic but it also can be therapeutic, helping to relieve pain and swelling caused by a buildup of joint fluid. Normal synovial uid is colorless and clear. Other noninfectious causes of arthritis that can occur in kids and teens include juvenile idiopathic arthritis (or JIA, formerly called rheumatoid arthritis, or JRA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and Lyme disease. It is a serious illness that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Septic arthritis causes symptoms like joint pain, swelling, redness, and fever. Joint aspiration helps to diagnose this condition.
It is usually due to a bacterial infection in the joint. Septic arthritis is a type of arthritis caused by an infection in the joint. Arthritis can cause redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in and around the joint, and difficulty moving the joint. Joint aspirations are most often done to help in the diagnosis and cause of arthritis (inflammation of a joint).

In a joint aspiration, a needle is carefully inserted into a joint space to collect a sample of synovial fluid.ĭoctors perform joint aspiration and examine the synovial fluid to evaluate for suspected diseases or conditions in a joint. Joints contain synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant to help them move easily. Joints are where two bones meet, allowing our bodies to move - the hips, knees, ankles, elbows, shoulders, knuckles, etc. A joint aspiration (arthrocentesis) is a test that involves withdrawing (aspirating) a small sample of joint fluid from a joint using a needle and syringe.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
